Myocarditis

Myocarditis
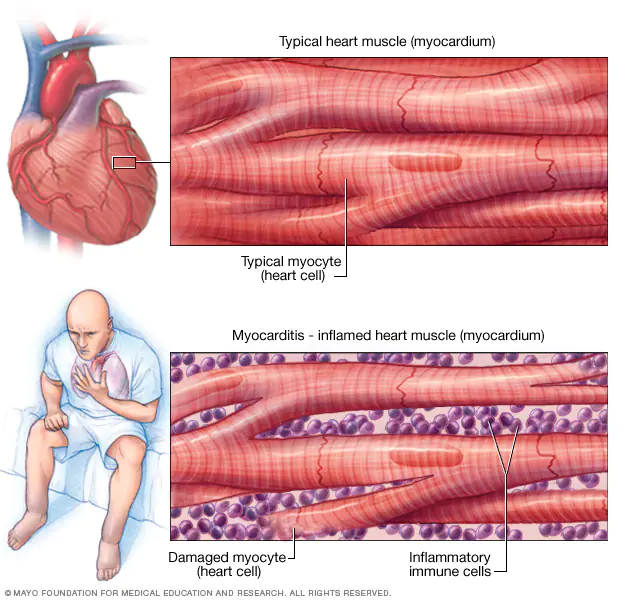
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle. This illustration shows a typical heart muscle compared to damaged heart muscle due to inflammation.
Overview
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium). The inflammation can reduce the heart's ability to pump blood. Myocarditis can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and rapid or irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
Infection with a virus is one cause of myocarditis. Sometimes a drug reaction or general inflammatory condition causes myocarditis.
Severe myocarditis weakens the heart so that the rest of the body doesn't get enough blood. Clots can form in the heart, leading to a stroke or heart attack.
Treatment for myocarditis may include medications, procedures or surgeries.
Symptoms
Some people with early myocarditis don't have symptoms. Others have mild symptoms.
Common myocarditis symptoms include:
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
- Swelling of the legs, ankles and feet
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmias)
- Shortness of breath, at rest or during activity
- Light-headedness or feeling like you might faint
- Flu-like symptoms such as headache, body aches, joint pain, fever or sore throat
Sometimes, myocarditis symptoms are like a heart attack. If you are having unexplained chest pain and shortness of breath, seek emergency medical help.
Myocarditis in children
When children develop myocarditis, symptoms may include:
- Breathing difficulties
- Chest pain
- Fainting
- Fever
- Rapid breathing
- Rapid or irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
When to see a doctor
Contact your health care provider if you have symptoms of myocarditis. Symptoms of myocarditis can seem like a heart attack. Get emergency medical help if you have unexplained chest pain, rapid heartbeats or shortness of breath.
If you have severe symptoms, go to the emergency room or call for emergency medical help.